Recently i spent a great deal of time studying about Virtualization and Cloud computing as part of work. I would like to share my understanding here.
When we listen to the words Virtualization and cloud computing, we may think that both are similar but they are completely different concepts. In order to achieve capital expenditure or CAPEX savings, virtualization was introduced.Virtualization software makes it possible to run multiple instances of operating systems and multiple applications on the same server at the same time. It enables businesses to reduce IT costs while increasing the efficiency, utilization and flexibility of their existing computer hardware.
Virtualization is software that manipulates hardware, while cloud computing refers to a service that results from that manipulation. Theoritically, cloud service can be offered based only on physical server without virtualization.This would result in providing induviual servers as a service which would be sub efficient compared to the service with virtualization.
In order to achieve operational expenditure or OPEX savings and increase efficiency of infrastructure, cloud service was introduced through automation, standardization and scale.Thus we moved from pure virtualization to introducing cloud stack/layer between application and virtualized hardware.
Let’s dig deeper into each of the topics now;
1. Virtualization
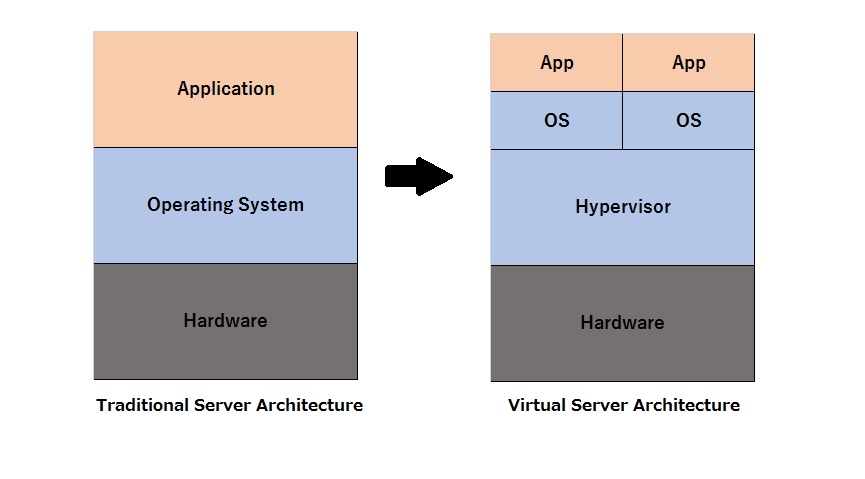
Virtualization is commonly hypervisor-based. The hypervisor isolates operating systems and applications from the underlying computer hardware so the host machine can run multiple virtual machines (VM) as guests that share the system’s physical compute resources, such as processor cycles, memory space, network bandwidth and so on.
Type 1 hypervisors, sometimes called bare-metal hypervisors, run directly on top of the host system hardware. Bare-metal hypervisors offer high availability and resource management. Their direct access to system hardware enables better performance, scalability and stability. Examples of type 1 hypervisors include Microsoft Hyper-V, Citrix XenServer and VMware ESXi.
A type 2 hypervisor, also known as a hosted hypervisor, is installed on top of the host operating system, rather than sitting directly on top of the hardware as the type 1 hypervisor does. Each guest OS or VM runs above the hypervisor. The convenience of a known host OS can ease system configuration and management tasks. However, the addition of a host OS layer can potentially limit performance and expose possible OS security flaws. Examples of type 2 hypervisors include VMware Workstation, KVM, EMU Vmware and Oracle VM VirtualBox.
The main alternative to hypervisor-based virtualization is containerization. Container virtualization (often referred as operating system virtualization) is more than just a different kind of hypervisor. Containers use the host operating system as their base, and not the hypervisor. Rather than virtualizing the hardware (which requires full virtualized operating system images for each guest), containers virtualize the OS itself, sharing the host OS kernel and its resources with both the host and other containers.
2. Cloud Computing
It is the method of building and providing on demand resources (memory, processor etc.,) over IP networks using data centers. Cloud computing enables companies/users to consume a compute resource, such as a virtual machine (VM), storage or an application, as a utility rather than having to build and maintain computing infrastructures in house. In other words, Cloud lets you trade CAPEX for OPEX ,i.e, you can pay only when you consume resources and on only how much you consume. Examples : AWS, Google docs/drive/app, Azure etc.
Some of the benefits of cloud computing:
• Self-service provisioning: End users can spin up compute resources for almost any type of workload on demand. This eliminates the traditional need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources.
• Elasticity: Companies can scale up as computing needs increase and scale down again as demands decrease. This eliminates the need for massive investments in local infrastructure, which may or may not remain active.
• Pay per use: Compute resources are measured at a granular level, enabling users to pay only for the resources and workloads they use.
• Migration flexibility: Organizations can move certain workloads to or from the cloud — or to different cloud platforms — as desired or automatically for better cost savings or to use new services as they emerge.
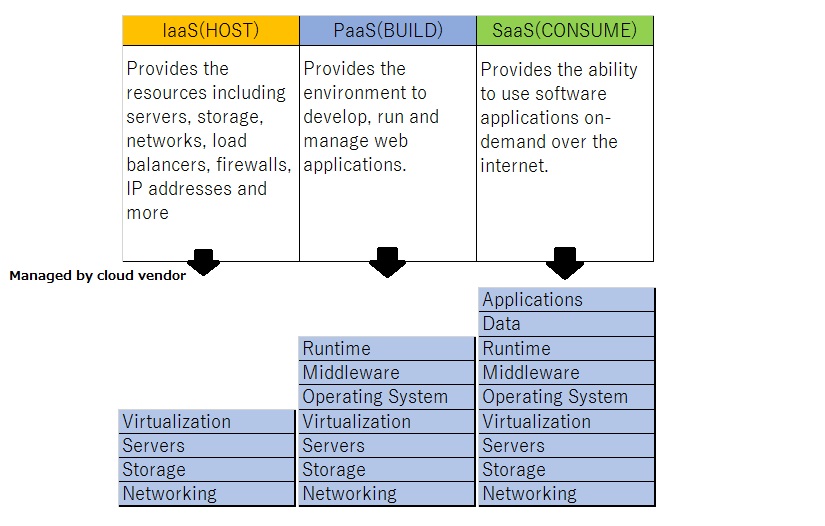
There are three main types of cloud service:
• Software as a Service (SaaS)
It is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network, typically the Internet.The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure.Examples: Google Apps, Micorsoft Office 365, Gmail, facebook.
• Platform as a Service (PaaS)
It is a paradigm for delivering operating systems and associated services like web services etc over the Internet without downloads or installation.The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure like servers, OS etc, but has control over the deployed applications and possibly configuration settings for the application-hosting environment.Examples: Tomcat, Google App engine, Apache Stratos.
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
It involves outsourcing the physical or Virtual machines used to support operations, including storage, hardware, servers and networking components.The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure but has control over OS, storage and deployed applications.Examples: AWS, Microsoft Azure,Google compute Engine.
Let me sum up the service models as follows;
The cloud service can be deployed based on a particular model. A cloud deployment model represents a specific type of cloud environment, primarily distinguished by ownership, size, and access.
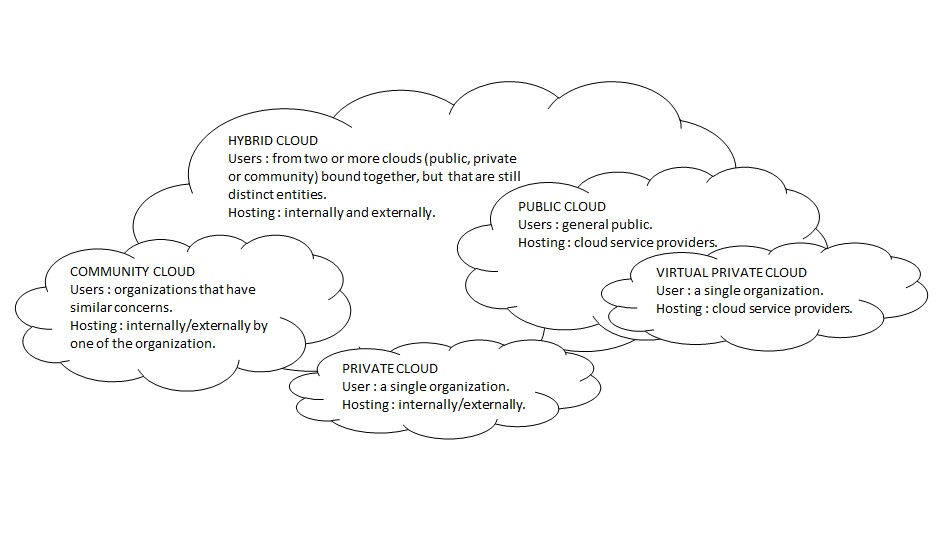
Some of the common cloud deployment models:
• Public Cloud
The most common and well-known deployment model is Public Cloud. A Public Cloud is a huge data centre that offers the same services to all its users. The services are accessible for everyone,i.e, open access and much used for the consumer segment. Examples of public services are AWS, Google, Yahoo, Office365 etc., For consumers, Public Cloud offerings are usually free of charge, for professionals there is usually a per-per-use (or user) pricing model. The Public Cloud is always hosted by a professional Cloud supplier.
• Private Cloud
A private cloud is cloud infrastructure that only members of your organization can utilize. It is typically owned and managed by the organization itself and is hosted on premises but it could also be managed by a third party in a secure datacenter. This deployment model is best suited for organizations that deal with sensitive data and/or are required to uphold certain security standards by various regulations.Example of Private cloud are Amazon VPC(Virtual Private Cloud), VMware Cloud Infrastructure suite.
• Community Cloud
This is the model where the cloud infrastructure is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). It may be managed by the organizations or a third party and may exist on premise or off premise. Example of community cloud being Google Apps for the government,Microsoft Government Community Cloud.
• Hybrid Cloud
This type of cloud infrastructure assumes that you are hosting your system both on private and public cloud. One use case might be regulation requiring data to be stored in a locked down private data center but have the application processing parts available on the public cloud and talking to the private components over a secure tunnel.
Another example is hosting most of the system inside a private cloud and having a clone of the system on the public cloud to allow for rapid scaling and accommodating bursts of new usage that would otherwise not be possible on the private cloud.To sum it up, we can say that it is a combination of public, private or community cloud models. Examples of Hybrid cloud being Windows Azure, VMware vCloud.
• Virtual Private Cloud
Virtual private clouds offer scalable compute resources similar to that of public clouds, but in a more controlled environment.To be more specific, a virtual private cloud (VPC) is the logical division of a service provider’s public cloud multi-tenant architecture to support private cloud computing in a public cloud environment. Public cloud providers like AWS, Google, Microsoft offer the possibility of setting up a VPC using virtual networks.
You can get the overall picture of the various deployment models as follows;
Check out my other blogs for further reading.,
Sources :
Online Learning

Leave a Reply