Introduction
The IT infrastructure in organizations today is an outgrowth of decades of evolution in computing platforms.The most recent eras are the general-purpose mainframe and minicomputer computing, personal computers, client/server networks, and the current enterprise and Internet computing.These eras do not necessarily end for all organizations at the same time, and the technologies that characterize one era may also be used in another time period for other purposes. For example, mainframe computers today are used as massive servers supporting large Websites and corporate enterprise applications.

Enterprise Internet Computing
The success of the client/server model posed a new set of problems for corporations. Many large firms found it difficult to integrate all of their local area networks (LANs) into a single, coherent corporate computing environment. Applications developed by local departments and divisions in a firm, or in different geographic areas, could not communicate easily with one another and share data.
As the Internet developed into a trusted communications environment, business firms began using the Transmission Control Protocol/ Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) networking standard to tie their disparate networks together. The resulting enterprise networks link mainframes, servers, PCs, mobile phones, and other handheld devices across the organization and between the firm and other organizations for free flow of information and also connect to public infrastructures such as the telephone system, the Internet, and public network services.
A Basic Enterprise LAN Network Architecture
The below diagram shows you the connectivity architecture of the major components that form an enterprise network.

LAN Architecture Sketch and Components
The Internet cloud refers to the source of the Internet to an organization. The organization could be connected to the Internet via Internet Leased Lines/ Broadband/ 3G etc. For connectivity to other branches, a VPN Network over the Internet could be used.
Before going ahead with the description of other components, lets get to know about switches. Network switches are always seen in data centers or server rooms for data transmission. Switch is used for linking the network devices together and switching the data from one port to another based on information from the packets being transmitted. The information complies with the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) seven-layer model to ensure product interoperability.

OSI seven-layer model
As for small networks, Layer 2 switches might be a good option. However, most networks will combine the Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches. Layer 3 is more intelligent and provides all the functionality of Layer 2 networks. Layer 4 switch is the enhanced version of Layer 3 and provides higher class of service for controlling the network traffic.

The Enterprise Router is basically a Layer-3 Network device that connects disparate networks. It acts as a gateway between the LAN and the WAN networks and the Internet Leased Lines/ MPLS Circuits/ Managed Leased Lines/ Broadband networks are all terminated on the router. Some Routers support additional modules for secure connectivity to other branches through VPN, Intrusion Prevention and Content Filtering etc.
The Unified Threat Management Appliance (or software) is for providing gateway level network security for the various end points used in the organization.The UTM Devices provide the following network security options: Firewall, Anti-Spam, Anti-Virus, Content Filtering, URL Filtering, Intrusion Prevention (IPS), Virtual Private Network (VPN), Protection from Internet threats like Phishing etc.
A Core/Backbone Switch is generally a Layer-3 based Network Switch that connects to the various distribution switches, edge switches (through distribution switches / directly) using Optical Fiber Networks or UTP Copper cabling. They generally also connect to the computer servers (ERP, Web Server, Mail Server, Database Server, Application Servers, etc). The core switch is in the center of an enterprise network and it also provides Inter-VLAN routing.
A NAS Device refers to a Network Area Storage Appliance (This could also be a Storage Area Network, depending upon the storage requirements) where bulk of the files/ data are stored for the servers and individual users (PC’s) to access them over the network whenever required.
There are many access points to provide wireless (Wi-Fi) access to the PC’s/ Laptops/ Wi-Fi Phones in the enterprise. All these Access Points are managed/ controlled by an appliance called ‘Wireless Controller’ which provides centralized authentication and other functionalities required for the wireless users across the network. The IP Telephony Server provides the call control functions (voice switching) for the telephony operations in an enterprise network. Since the IP Phones connect to the computer networks, these IP Telephony Servers provide centralized administration and connectivity to PSTN Lines to all the IP Phones/ VOIP devices over the network.
Enterprise IT
Enterprise IT includes the technology staff, services, and support associated with enterprise systems and services, as well as their strategy, management, budgets, and policy. Enterprise IT also includes many of the infrastructure and services that companies or institutions use to store and manage data and processes, regardless of whether they are hosted on campus, in the cloud, or through shared services. It primarily has an administrative focus rather than one of research. Because it deals with core organizational business activities, enterprise IT is central to the success of any company or institution. In the below picture, one can get an idea of all the components like the development of enterprise IT, testing the same and implementing. Once implemented, the support team needs to provide the users with support relating to application or system issues.

One of the main component here is Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) as well, which is a type of business planning that relates to business intelligence (BI), which involves evaluating and managing performance for an enterprise to reach performance goals, enhance efficiency or maximize business processes. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) can be said to be a part of EPM.
Management of these core organizational services goes beyond just taking care of the technology. For example, as institutions move services into the cloud, the responsibility for managing the service remains a responsibility of enterprise IT. The transition from on-premise to cloud causes IT to shift focus and concentrate on contract management, vendor relations, collaborations with functional and business units, and data integration issues.
Our focus here will be on ‘end user support’ or the ‘application and system operations support’ which mainly includes IT Service Desk Support, Desktop Management Services etc.
Application and System Operations Support
Enterprise support services manage the daily activities to keep end users PC, applications and related infrastructure highly available and secure which ensures the organization to focus on its own core business.
Desktop Management Services & IT Support
BMC Remedyforce:
A best-practice approach to the management of incidents, problems, service requests, and tasks. The relevant data for any record is displayed in a visual format, making it easy to access all related information to fulfill a request. See which tasks are open, pending, or closed and get details about the record’s action history as well.
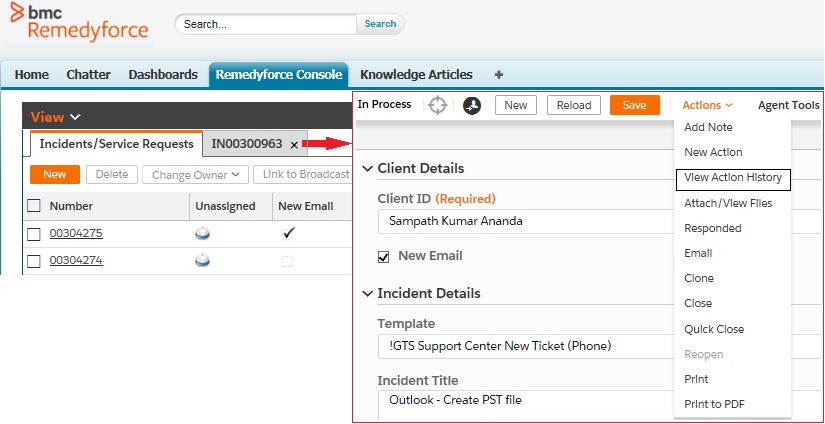
BMC Remedyforce
There are various user applications used at organizations, like the MS Office, Adobe Acrobat, Document Manager, Sharefile, Skype for Business etc., as well as OS regarding which issues or queries may come up and would require IT support team to address them. So when a user request or escalation comes up, the best practice approach of handling the requests in the form of tickets is used so that the issue can be resolved by the concerned IT support team or can be routed to the next level IT support team for better handling of the issue.
The generation of a new ticket w.r.t a user request would involve inputting the following sections;
Client ID/Name, Incident Title, Description, Category, Impact, Priority, Incident Source, Incident Type ,Urgency, Status, Date and Time, Queue, Staff
OS Image Install:
The computer must be connected to the LAN network when re-imaging a managed computer/laptop. Restart the computer. Click on F1 to enter the bios menu. Here the standard setting under Startup “UEFI/Legacy Boot” would be Legacy Only or both. Security “Secure Boot” to be set to disabled and “Security Chip” to be made active and to be set to 1.2 TPM. Save the setting and press F12 to enter the boot menu. Once you arrive at the boot menu, select the option to boot to the Onboard Network Interface Card (NIC). Upon arriving at the next screen, enter the necessary password if any. Next, it’ll prompt you to “Select the operating system you want to install” – choose the appropriate installation image (operating system) for that type of computer. The installation is expected to complete in a couple of hours in case of no issues.
Once the OS is setup and the user credentials are received from the Active Directory administrator, login using the user credentials and check whether the necessary applications are installed properly and also do the necessary setting which allows remote login with or without permissions. Use the desktopadmin login to perform the necessary settings or to do the group policy update.
Symantec Encryption Server Administration:
Symantec™ Encryption Management Server is a console that manages the applications that provide email, disk, and network file encryption. Symantec Encryption Desktop, a client product, creates PGP keypairs , encrypts user email, encrypts entire, or partial, hard drives etc. This is mainly used when WDRT’s are to be generated. Whole disk recovery tokens (WDRTs) are a means by which an encrypted device is accessed once a user has been locked out or has forgotten their password. This is especially valuable when the device is not in the same location as the administrator.
System Center Configuration Manager:
Configuration Manager console provides remote control, patch management, software distribution, operating system deployment, network access protection and hardware & software inventory. Once OS is installed on a PC we can see the PC getting listed on SCCM which must be deleted inorder to perform re-installation of OS image on the same PC the next time in case of need. Once the device is detected on SCCM, set the device as a primary device for the user.
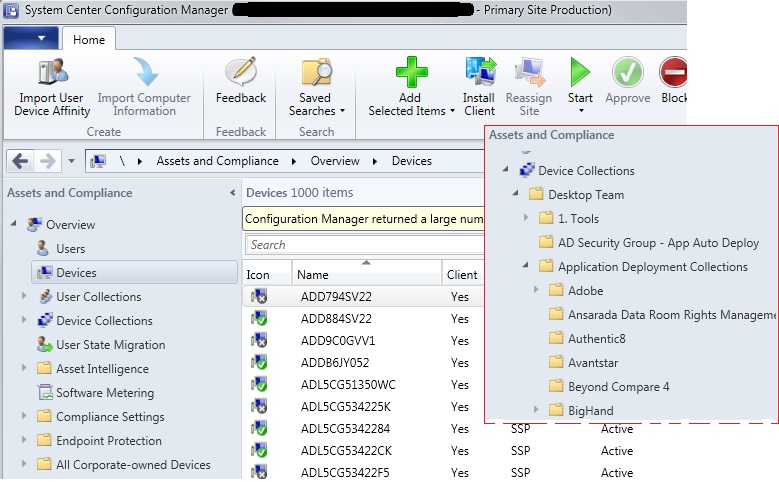
Configuration Manager Console
In case we need to push a new application or a patch which is present on SCCM to a PC remotely, we can go to the respective folder as shown inside the red frame in the above picture ,i.e, “Device Collections > Desktop Team > Application Deployment Collections” > Application name > Application Installation > Deploy Device item. Now right click on the options to select “Add Resources” , type in the PC name here to push the application install which might take time to install on the remote system. Also click on “Client Notifications > Evaluate Application Deployments” to cross check the installation.
Configuration manager can be configured to deploy content to a device based on the primary device setting.
Proxy Master & Proxy Pro Host Control Panel:
PROXY Pro Master is a program developed by Proxy Networks. It allows administrator to view and operate PROXY Pro Hosts. PROXY Pro Host application enables the desktop/laptop of a Windows PC or server to be viewed and controlled remotely. As shown in the below figure, five devices can be viewed to be online and can be controlled by the administrator by clicking on the respective item to remotely perform any activity on the user’s PC. In case we want to access the PC which is not displayed in the list, just type in the PC name or IP address in the “Station” box to search the PC and remotely login to the online PC.
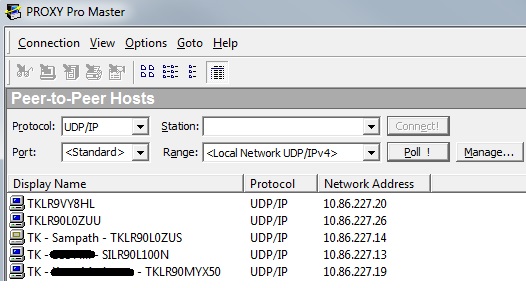
Proxy Pro Master Application
Proxy Pro Host Control Panel is basically installed on all the PCs. The client/user access permission can be set so that the administrator can remotely access the PC with/without permission. Here the client/user PC name can be changed on the user’s PC so that we should be able to recognize the correct user name on the Proxy master window while remoting on to the user’s system.
ForeScout CounterACT:
In response to enhanced client security requirements, a new technology to protect the firm’s network from unauthorized computers and other devices. Such devices could be used to gain access to sensitive data belonging to the firm and clients, so going forward only devices which are recognized as our company supplied devices will be able to gain network access.

ForeScout Application
ForeScout will be enabled and lock out machines that do not pass internal compliance: If any of these applications / key is not present or modified(not to standard) ForeScout will go ahead and lock the machine out of the network.
•Tanium (Investigation Software)
•Symantec EndPoint (Antivirus)
•Cylance (Antivirus)
•Cyber Reason (Investigation Software)
•A registry key
In case of any PC blockage due to known modifications or issues which can be checked under the compliance tab at the center of the screen, the blacklisted PC can whitelisted on the ForeScout Application by the administrator.
Cisco IP User phone:
Cisco Unified Communications Manager (CUCM) administrative page is accessed to perform moves, adds, and changes of Cisco IP phones, while configuring users and associating them with phones. Configuring simple features, such as DND, Music on Hold, as well as access to CUCM user web pages can be done. Cisco Expansion module configuration can also be done using CUCM.
Cisco Unity Connection Administration tool is used in most of the administrative tasks such as, customizing user settings(voice messaging, mailbox storage etc) and implementing a call management plan. Unity Connection Administration also provides access to several other tools including the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT), Custom Keypad Mapping, Task Management, and Migration Utilities.
We already know that IP Phones connect to the computer networks and they do so through VLANs similar to PCs. To brief about VLANs, they are a method of creating logically-independent networks within a huge network interconnected through switches. A VLAN consists of a network of computers that behave as if connected to the same wire – even though they may actually be physically connected to different segments of a LAN. Several VLANs can co-exist within such a network. This helps in reducing the broadcast domain and therefore the effects of broadcast storms, worms and viruses, and Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. VLANs are therefore often deployed to improve the overall system performance and availability, which are important security considerations. IP Phone connection illustration: Cisco IP Phone connect to PoE network point through LAN cable which inturn connects to VLAN10(Layer 2 segment) port in the server room.
Mobile Device Management:
The IBM® MaaS360® Mobile Device Management (SaaS) is an enterprise mobility management (EMM) platform that provides visibility and control of smartphones and tablets in the enterprise. The IBM MaaS360 software supports devices such as iPhone, iPad, Android, and Windows Phone.

IBM MaaS360
The above figure shows the administrative screen of MaaS360 application. Either the firm issued mobile device or the self owned device can be configured using this application for any user. Once the device registration link is accessed from the mobile device, MaaS360 mailbox will be installed automatically which can be used to check corporate emails or perform secure browsing with the MaaS browser.
Power Outage Support:
Sometimes there will be a need to switch off all the devices of the organization which includes the server room as well due to some maintenance activity or power outage. So one needs to make sure each employee switches off his/her PC and other associated devices beforehand. Moving on to the server room activity of the branch/main office, the virtual machines(VM) running on the servers need to be turned off followed by the shutdown of servers with UCS and finally the storage array devices using the concerned application by IT support staff with administrative access. During power outage, the DNS server routing will be changed to data center from the local server. Once the outage activity is complete, the storage arrays, servers and VMs need to be restored and the network access need to be checked by turning on the PC and other associated devices.
The Cisco Unified Computing System is a next-generation data center platform that unites compute, network, storage access, and virtualization into a cohesive system designed to reduce total cost of ownership (TCO) and increase business agility. Virtualization helps data centers the most when servers are configured into resource pools that can be harnessed on demand to meet fluctuating workload requirements; deploy new applications without tying them to specific hardware; and move virtual machines between servers to balance workloads, meet service-level agreements (SLAs), or prepare a server for scheduled downtime. Cisco UCS Manager transforms the resources of the Cisco Unified Computing System into a single cohesive system that is ideal for establishing resource pools for virtualized environments.
Finally coming to one of the most important Microsoft service ,i.e, the directory service that Microsoft developed for the Windows domain networks called the Active Directory(AD) as mentioned in the OS image install section. Starting with Windows Server 2008, Active Directory became an umbrella title for a broad range of directory-based identity-related services. A server running Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is called a domain controller. It authenticates and authorizes all users and computers in a Windows domain type network—assigning and enforcing security policies for all computers and installing or updating software. For example, when a user logs into a computer that is part of a Windows domain, Active Directory checks the submitted password and determines whether the user is a system administrator or normal user. Also, it allows management and storage of information, provides authentication and authorization mechanisms, and establishes a framework to deploy other related services.
Credits:
Knowledge, Experience

Leave a Reply