Software is a set of instructions, programs, or data that tells a computer or device what to do and how to do it, enabling it to perform specific tasks, unlike physical hardware which you can touch. There are two main types of software, namely, the Operating system and Application software. Application software runs on top of the Operating system and uses the computer’s resources to perform a task. In this modern era, software is being used in every industry, making its correctness essential to the proper functionality of everyday life.
Software companies aim to deliver a high-quality product on time and under budget. This is where software testing becomes imperative to deliver a quality product. Software Testing is a systematic process of evaluating an application to identify defects, bugs, or deviations from the expected behaviour. It is fundamentally a process of verification and validation. For valid results, tests must be performed in environments that closely resemble the production environment, using similar infrastructure and data. High-quality products are never an accident; they are the result of deliberate, intelligent effort in development and testing.
Software Testing & STLC
Similar to the SDLC for creating software, there is STLC for Software testing, which needs to be followed by testing teams to ensure software quality. Skipping the testing phase can negatively impact both the product and the brand’s reputation. The six phases of STLC are: Requirement analysis, Test planning, Test case development, Environment setup, Test execution, Test cycle closure. The testing process is categorized into three primary levels as follows, moving from granular components to the entire system.
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- System Testing/E2E test
Functional testing focuses on what the system does (features wrt requirements), while non-functional testing focuses on how it performs (speed, reliability and security). We have the Unit testing, Integration testing, System testing(E2E test), Interface testing, Regression testing and UAT under functional testing. While the documentation testing, installation testing, performance testing, reliability testing, security testing fall under non-functional testing.
Manual or Automation testing is utilized for the above based on strategic purpose. While manual testing is used in the areas where exploratory, human judgement and subjective human experiences are needed. On the other hand, automation testing is used where speed, reliability is needed. Even for repetitive tasks and complex end to end workflows Automation testing is used.
AI-Powered Testing
AI can act as a Co-pilot to the tester in the following areas of STLC. This can be for Test case generation, Test automation scripts, Test data generation, Test maintenance, prioritisation, and exploratory testing ideas. It is important to note that blind copy-paste of AI output without human verification is dangerous. AI generated test cases can sometimes be broad but lack the necessary depth.
Playwright Framework & Tools
Playwright is a powerful and versatile automation library developed by Microsoft. It enables developers and testers to automate web applications across multiple browsers with ease. Playwright’s architecture is designed to provide a robust, flexible, and high-performance framework for browser automation. It is preferred over older frameworks like Selenium for writing end-to-end test automation scripts.
If you are using a Windows PC, select the necessary option/s and download the latest Node.js using the following link, which is a prerequisite for installing Playwright. Even npm installation is a prerequisite.
Once the download and installation are complete, use the following commands to check whether it is installed properly or not. The commands can be used in the command prompt or in the Terminal section of VS Code IDE to verify the versions installed. Here, “npm” refers to Node Package Manager.
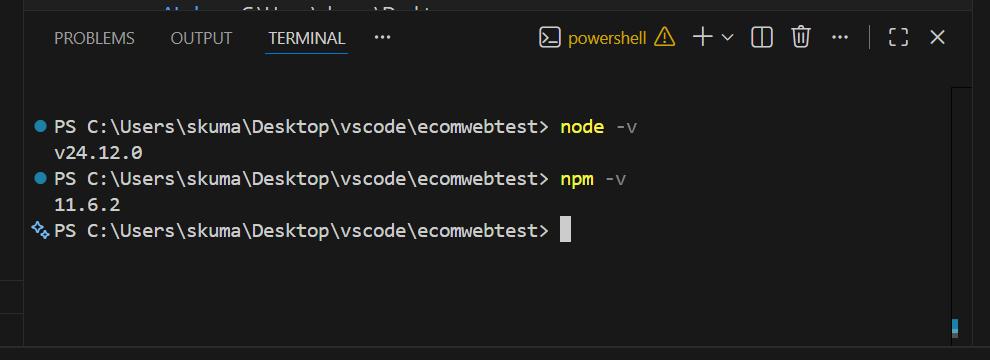
If you need to download and setup VSCode, use the following link to download and perform the installation.
On VS Code, click on “Open Folder” to navigate to an existing folder or create a new one (ECOMWEBTEST) and Open it. We will now go through the following link for more details on playwright setup.
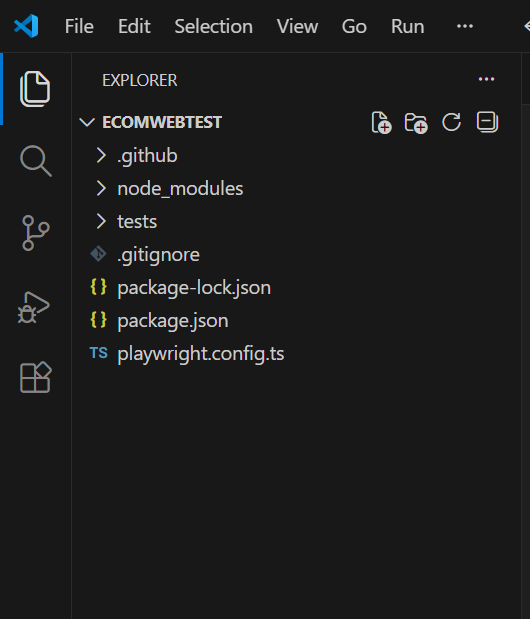
As mentioned in the above link, the following command adds Playwright to the existing project/folder on VS Code if it is not yet setup. Once the following command is executed, you can see the folders/files as displayed in the below picture to get populated under the folder ECOMWEBTEST.
npm init playwright@latest
Test Case Generation
Now that we have set up Playwright in VS Code, let us use an AI tool (OpenAI/Claude etc) to generate Test cases for a sample scenario using the following prompt.
"Consider yourself as a QA testing expert. Generate detailed test cases for saucedemo.com login and checkout flow. Include positive and negative scenarios. I will be using playwright in order to test this."
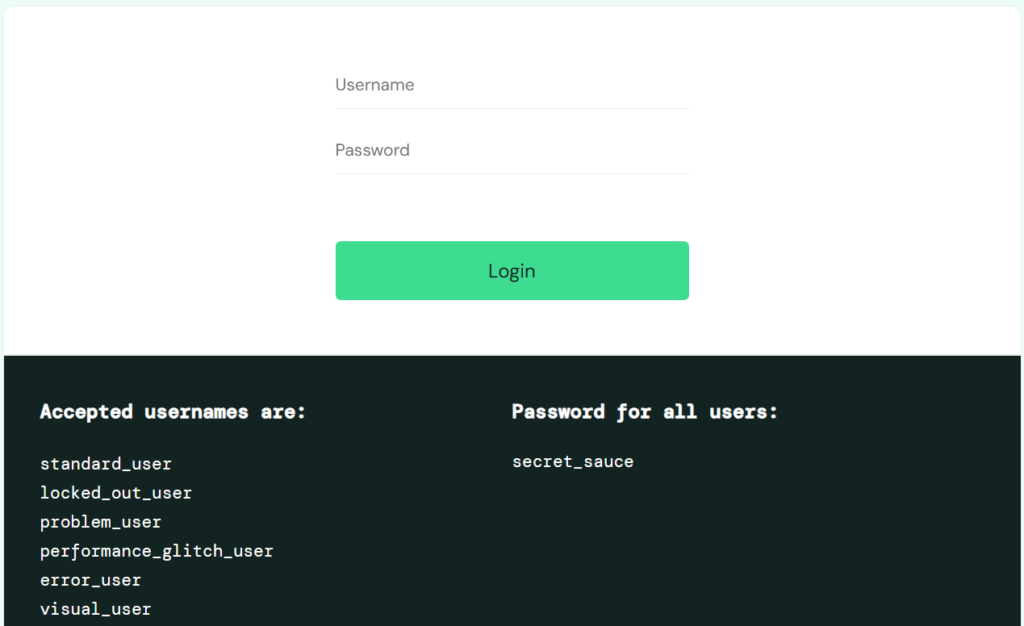
After all the test cases are generated using the above prompt, we will move on to the execution of the test cases.
Test Case Execution
As you are inside the project folder on VS Code, you can refer to the below prompt result to gain insights on how to run the tests.
"I am inside a folder in VS Code. Guide me on how to run the tests listed above."
From the result of the prompt in the earlier section, copy and paste any one of the test cases into the code file. For example, let us copy the code for login test into the newly created code file under tests folder. The name of the file is set to saucedemo.spec.ts as shown in the below picture.
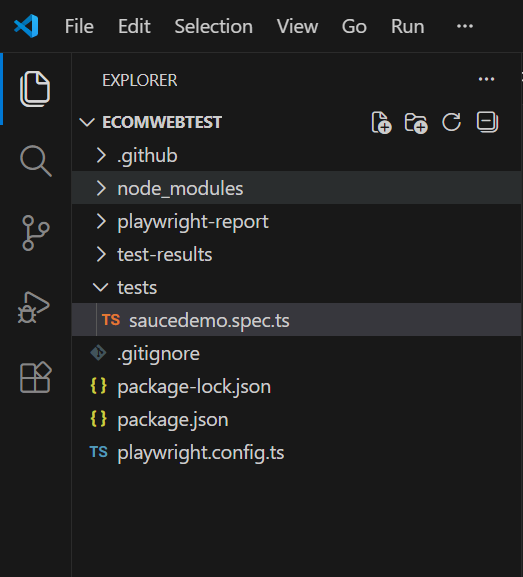
The code to test the login (generated by AI tool) is as follows. Check the code to confirm whether the website name is mentioned or not.
import { test, expect } from '@playwright/test';
test('Successful login with valid credentials', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('https:www.saucedemo.com/');
await page.fill('[data-test="username"]', 'standard_user');
await page.fill('[data-test="password"]', 'secret_sauce');
await page.click('[data-test="login-button"]');
await expect(page).toHaveURL(/inventory.html/);
await expect(page.locator('.inventory_item')).toHaveCount(6);
});
Execute the above code by using the following command.
npx playwright test tests/saucedemo.spec.ts --headed
Headed Mode enables testers to visually verify automated actions, such as typing and clicking. Whereas the other mode, i.e, Trace Viewer provides a step-by-step trace of every action for verification. Once you press the enter key, the code will automatically run and execute the login for multiple browsers (Chrome, Webkit and Firefox). On successful run, you will get the following output under the Terminal section.
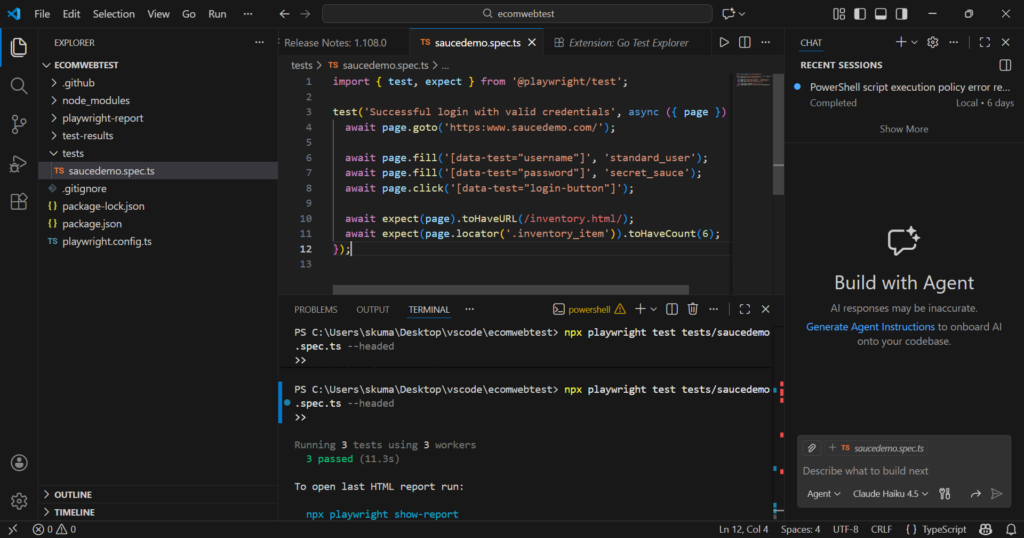
In case the test is a success as shown above, move on to the next test case. Similar to the first test case, execute the code for other tests using different file names.
Further Reading:


Leave a Reply