Purpose
The most common cause of workplace accidents or industrial accidents is often attributed to human error such as operational error, judgmental error, and job-related error, all of which are caused by human characteristics. Human behavioral characteristics, such as mistakes and carelessness, are called “human characteristics,” and errors caused by human characteristics are called “human errors.”One more major effect of human error is that it leads to interruption of services to customer, resulting in loss of trust and/or compensation for damages.
Work is always accompanied by issues related to human error, and unsafe behavior accounts for about 90% of all accidents, including those caused by inexperienced and unskilled workers.Most of the human errors are said to be associated with psychological factors affecting human behavior like carelessness and assumption based work.
Specific safety methods were developed so that workplaces can take steps on preemptive action for safety which includes hazard prediction training and pointing and calling. Activities incorporating these methods in a unified manner are called hazard prediction activities and will result in improved customer satisfaction.
Below points need to be kept in mind while doing any work;
• Take appropriate measures beforehand in order to counter risk after identification.
• Recheck at each of the important stages of work.
• Do the things that are obvious and need to be done.
• Human error reduction through Team work and communication.
Human Error and Hiyari Hatto
Human Error : An inappropriate or undesirable human behavior or decision that reduces, or has the potential for reducing, effectiveness, safety, or system performance resulting in trouble, accident or escalations.
Undesirable or inappropriate human behavior can be anything concerned with human nature like misjudgement, mishearing, verbal slip-up, misunderstand, carelessness. Even risk taking factors like rule violation wherein difficulty to abide, probability that it is ok to violate as others are doing can also be categorized as inappropriate behavior.
Hiyari Hatto (HH) : An inappropriate or undesirable human behavior or decision that reduces, or has the potential for reducing, effectiveness, safety, or system performance but didn’t result in trouble, accident or escalations.
Hiyari Hatto is a Japanese term. It means Experience of Almost Accident situation. Hiyari Hatto (HH) is a System to
• Identify the possible danger through Team members experience
• Develop the countermeasure utilizing their expertise and
• Implement the same in consultation with Team members supervisor
It is a pro-active exercise but not post mortem after accident.
What is HEZ Activity/Campaign
Each and every individual human being is irreplaceable. The HEZ(Human Error Zero) Campaign aims for zero accidents in the workplace resulting in increased customer satisfaction.The Campaign builds on the three principles of zero accidents, preemptive action, and participation to implement the KY activity in order to prevent human errors and bring about increased customer satisfaction.
The three principles
The following are the three basic principles.
The principle of zero accidents
“Zero accidents” means to achieve an accident free workplace (not only no fatal accidents or accidents causing absent from work, but also no accidents, including industrial accidents, occupational illness, or other accidents) by detecting, understanding, and solving all hazards (problems) in everybody’s daily life as well as potential hazards existing in workplaces and work and should be implemented 100%.
The principle of preemptive action
“Preemptive action” means to prevent all accidents and industrial accidents by detecting, understanding, and solving all hazards (problems) in everybody’s daily life as well as potential hazards existing in workplaces and work in order to create a brighter and more vigorous workplace with zero accidents and zero diseases as an ultimate goal.
Here the basic understanding is that, counter measures need to be developed for hiyari hatto which may lead to accidents or trouble. On the other hand, unsafe actions which may lead to hiyari hatto should also be identified beforehand and appropriate counter measures be taken. Also in situation where accident has happened already, the causes need to be found out in order to avoid re-occurrence.
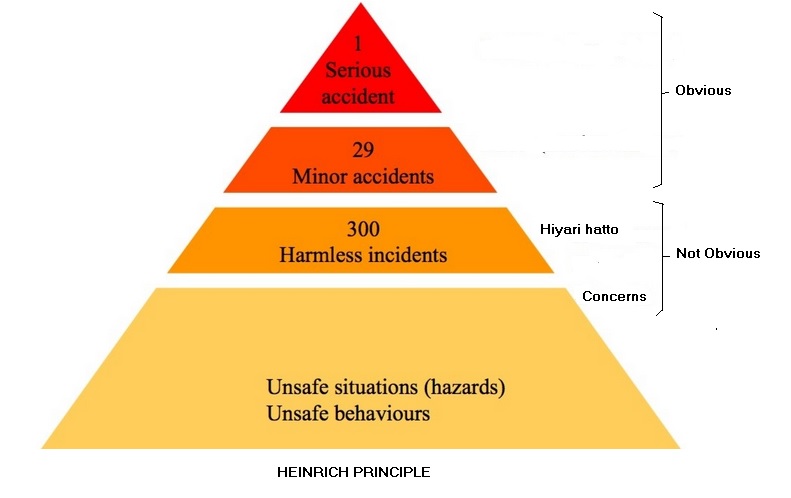
As per Heinrich’s findings for every accident that causes a major injury, there are 29 accidents that cause minor injuries and 300 accidents that cause no injuries or “near misses.” He felt that because accidents share many common root causes, addressing the commonplace accidents will help eliminate major injuries or fatalities down the road. Heinrich also believed from his findings that 85 to 95% of all workplace accidents stem from unsafe actions by individuals.
The principle of participation
“Participation” means to make a concerted effort by managers, supervisors, staff, and workers to detect, understand, and solve potential hazards (problems) existing in workplaces and work. It requires the voluntary effort and commitment of all those involved in actions for problem-solving.
Hazard Prediction Activity(KY Katsudo)
*KY Katsudo (K: kiken (hazard), Y: yochi (prediction), Katsudo: Activity)
Hazard Prediction(KY) Activity is a brainstorming drill to discuss, mutually consider and understand all potential human error factors in advance. The potential human errors can rise out of human trait like carelessness (misjudgement, mishearing etc) and risk taking activities like rule violation(follow the crowd, assumption based work etc). The purpose of KY activity is to detect possible human errors beforehand or even in the case of human error should not result in affecting customer services. This activity is used in the promotion of HEZ campaign.
Here you can find a sample of KY Activity chart used during the brainstorming drill, just before start of work.

HE Preventive Measures
In order to tackle accidents caused by human error the following three preventive measures must be ensured:
Hardware (equipment, facilities, and other tools)
It is important to push ahead with safety and health measures in terms of Fail Safe or Fool Proof hardware (facilities, machinery, working environment, and raw materials) for the prevention of accidents caused by human error.
Software (human beings as well as hardware)
In addition to the above measures, it is necessary to improve the working environment including the relationship between workers and hardware as well as work from the perspective of a man-machine system. Here necessary procedure document should be created with checklist sections for the creation, implementation and confirm operations. An environment wherein 4S is implemented would be the best.
Humanware
Humanware incorporates the safety and health management of both hardware and software. Effective humanware hazard prediction activities incorporate countermeasures against human error and include the Health KY, the hazard prediction training (KYT), pointing and calling and the Hiyari hatto.
All the three,i.e., Hardware, Software and Humanware countermeasure put together will result in achieving the goals of HEZ campaign.
HEZ Activity in detail
Here i will take you through the specific actions which must be performed in-order to create a Human Error Zero environment.
 (1) HEZ training to all the employees of a company
(1) HEZ training to all the employees of a company
Appropriate HEZ training to all the employees at different levels of a company needs to be provided. This can go a great way in creating awareness and reduce the Human error at work and eventually make it reach the ideal zero figure.
(2) Strict adherence to the code of conduct at work
While any work is done with the elementary action items being put into practice, the must be adhered to rules should be kept in mind and is known as the code of conduct at work. In any organization, the code of conduct will be released and distributed as either a booklet or a card along with a briefing session regarding the same. The code of conduct document will contain the code of conduct items, concrete examples relating to code of conduct and the definition of terminologies.
The elementary action items are nothing but the consolidated number items of any organization based on the past occurrences of operation error or accidents and is the compilation of preventive measures with respect to the same. A few of the elementary action items are KY drill before start of work, work to be executed as per the procedure document, pointing and calling at each of the important points, contact concerned authority in case of ambiguity or insecurity or abnormality after stopping the work etc.,
(3) Hiyari Hatto activity
In order to target zero HE, the potential accident causing condition should be grasped in advance and procedure should be established to report as many as such cases to the management as possible. Also let’s ensure that countermeasures are taken to all HH in-order to make work place safer, pleasant and easy to work. The below flow chart shows a sample pictorial representation of the HH activity work flow.
 (4) Pointing and Calling in every day activity
(4) Pointing and Calling in every day activity
This activity involves pointing at target objects by stretching your arm and stating out loud, “Such and such is OK” at important points in the work in order to proceed with work safely and correctly. Pointing and calling are methods for raising the consciousness level of workers and confirming that conditions are regular and clear, increasing the accuracy and safety of work.By raising the consciousness level, accidents resulting out of human characteristics of carelessness like misjudgement, mishearing etc., can be avoided.

A few illustrations of the pointing and calling are as follows;
Eg 1) email address confirmation before sending a email – abc@xyz.com address Yoshi!
Eg 2) Cabinet confirmation before leaving your work desk at break time – 1/2/3 desk cabinet/s locked Yoshi!
Eg 3) Tidiness confirmation after finishing work at the end of day – clear desk Yoshi!
Eg 4) Avoiding forgetfulness before moving out – possess a/b/c Yoshi!
The results of proof testing conducted by the Railway Technical Research Institute in 1994 showed that the rate of work-related errors decreased to less than one-sixth when conducting pointing and calling as compared with doing nothing.
(5) Hazard Prediction Training(KYT) at workplace
Hazard prediction training called ” Kiken-Yochi Training ” (KYT) in Japanese can be defined as a role-play based training method, in which staff members first observe photos/videos or illustrations of everyday scenes in a workplace, and then those scenes are discussed within a group for detection of potential hazards, countermeasures against hazardous issues , and, finally, slogans or messages are created and directed at risk avoidance (ensuring of safety). It was invented in 1974 in Japan for prevention of occupational accidents, and, since the late 1970s, has spread from the manufacturing industry to the entire industrial world. A systematic review reported that KYT reduced the occupational accident rate significantly. Thereafter, KYT was introduced into safety education programs across industries, leading to a significant reduction in accidents.
The KYT Basic 4-Round Method forms the foundation for this activity. Participants openly discuss the hidden hazards depicted in the illustrations of the workplace and work conditions and solve problems by proceeding through the four rounds step by step.
Round 1: What are the hidden hazards? (Understanding the actual situation)
Round 2: These are the danger points. (Investigating the reality)
Round 3: What would you do? (Establishing countermeasures)
Round 4: These are the danger points. (Setting targets)
The KYT method increases the motivation of workers to practice in teams. It uses meetings to sharpen awareness of what constitutes danger. Workers share information on hazards and improve their problem solving capabilities by working on finding solutions in meetings. And they improve their powers of concentration by practicing pointing and calling activities in all of the important points in the work.
In order to maintain long term consistency in the implementation of KYT learnings, the following points should be kept in mind and executed during everyday activities.
1) Sensitivity towards the hazard points
2) Rise the concentration level through pointing and calling
3) Improve problem resolution through KY activity
4) Fire up the motivation through KY activity
5) Display teamwork in detection, understanding and resolution of problems during KY activity
6) Think the problems as your own
(6) Morning and Evening Assembly
In order to perform any task safely and avoid human errors one more important component would be to actively take part in the morning and evening assembly sessions. Other than being an integral part for the execution of everyday activities, here we can find various teams sharing their experiences which may include accident reporting, hiyari hatto incidents, new learnings etc. and thus serves as a place for self development.
KY cycle is a structure wherein Health and safety is integrated as part of everyday activities which includes the morning and evening assembly sessions. Here we can find the various safety techniques included in every work performed as well. Each KY cycle is divided into 3 parts ,i.e, safety measures taken before work, while doing work and after work activities and promotion of human error zero activity is done.

The above picture gives you the description of KY cycle of every day work and relates to every work performed in a day.
(7) Repetition & Reporting
Sometimes the output of our work may differ from the instructions received which was not cross checked. Also there may be times when we may have been asked about the status of work which was not reported. These two are instances wherein the repetition of the instruction received in the former case and reporting of the work status in the latter case are not adhered to.
Repetition(Before start of work)
This is a way of making sure the instruction is received correctly by repeating the instruction contents loudly. So we can get started with the work avoiding any potential human errors with respect to receiving instructions.
Reporting(After work)
This is a way to inform about the progress of work with respect to the instruction received. By this was both the receiving and instructing side can fell safe about the proper progress or completion of work.
(8) 4S(seiri, seiton, seiso, seiketsu)
4S is a workplace organization method abbreviated from the Japanese words seri for “Sort”, seiton for “Set in order”, seiso for “Systematic cleaning” and seiketsu for “Standardize”. Organizing the workplace leads to a safe and healthy environment.
• Sorting — separating the needed from the unneeded. Sorting activities aim to eliminate unneeded items from the work area and to perform an initial cleaning.
• Set in order — a place for everything and everything in its place, clean and ready for use. Simplifying arranges the workplace to ensure safety and efficiency.
• Systematic Cleaning — cleaning for inspection. Systematic daily cleaning and inspection of work areas and equipment help you understand current conditions and determine if corrective action is required.
• Standardize — developing common methods for consistency. Standardizing assures that everyone knows what is expected .It aims to make abnormal conditions noticeable and to document agreements to ensure consistency and sustainability.
The 3 main pillars of the HEZ activity
Implementation of the HEZ Campaign requires three important pillars: the positive attitude of the top management, the complete management of the safety and health system by line managers and supervisors, and the promotion of voluntary activities in the workplace. The HEZ Campaign depends on the mutual relationships and assistance of these three pillars.
1) The positive attitude of the top management
The starting point of safety and health activity is a tough attitude held by top management towards zero accidents and zero diseases.The campaign starts with a determined commitment by the senior management to respect every single worker and ensure no injuries.
2) The complete management of the safety and health system by line managers and supervisors
In order to promote safety and health in the workplace, it is essential for line managers and supervisors to lead by example by integrating safety and health activities into day-to-day work, making safety and health part of the line management.
3) The activation of voluntary activities in the workplace
Human error plays a part in most workplace accidents, and each and every employee needs to be fully aware that responsibility cannot be shifted to others. Employees must engage in small group activities for zero accidents with the awareness that their existence is irreplaceable for their families and dependents and safety and health is their own and their co-worker’s own problem.
Conclusion
The philosophy of the HEZ Activity is to respect human life. Specific safety methods are developed so that workplaces can take steps on preemptive action for safety. Activities incorporating these methods in a unified manner are called hazard prediction(KY) activities. As the system is operated by human beings, so, to make it function properly, it requires the motivation and enthusiasm of all of the people involved in it, namely the top management, the line managers, and the team members.
Sources:
危険予知訓練(KY Training), experience

Leave a Reply